Treatment Modalities
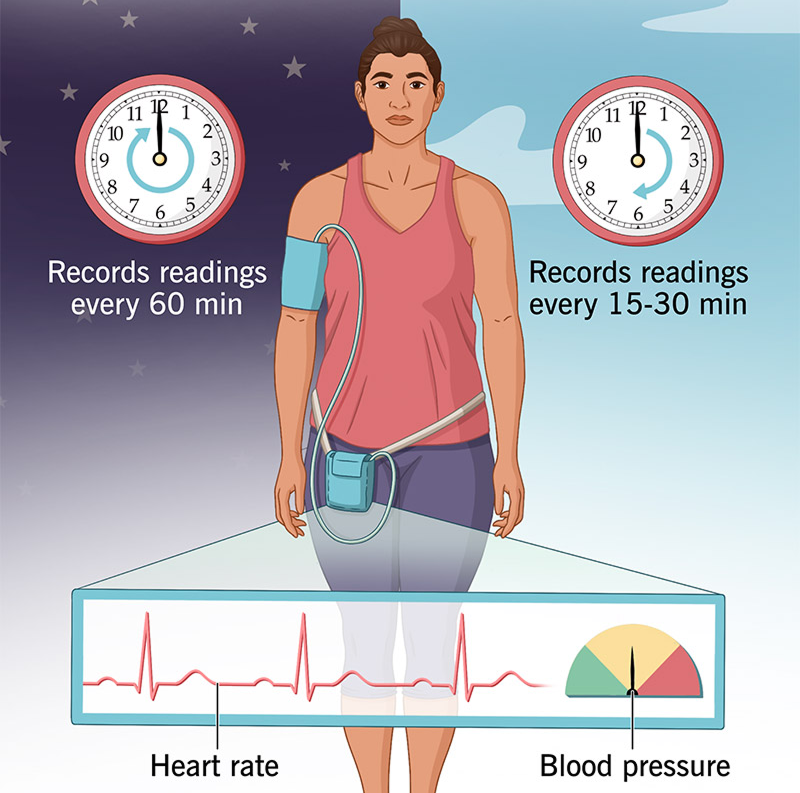
1. 24 hr ABPM
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring is a method to measure your blood pressure on a continuous basis for 24 hours. Your blood pressure is measured even as you sleep. The ongoing data helps your healthcare provider get a more accurate picture of your blood pressure numbers. The results can confirm a high blood pressure diagnosis and guide treatment.
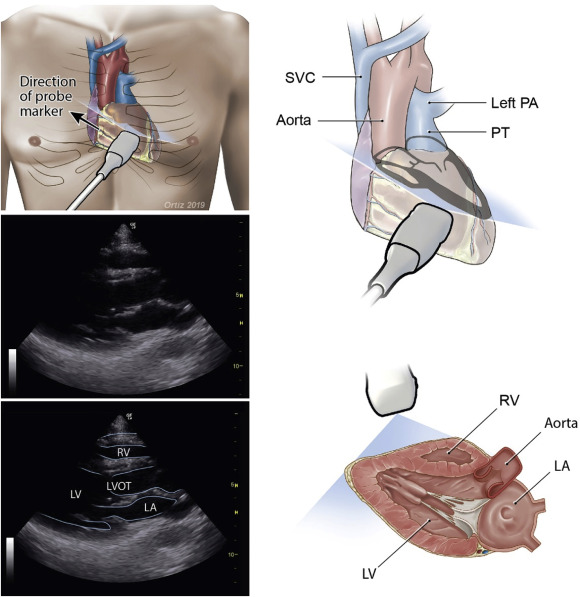
2. 2 D Echocardiography
2D Echocardiography shows the heart’s structure and function, helping assess pumping capacity and detect defects. Color Doppler adds blood flow imaging to spot valve leaks or abnormal flow. Stress Echo checks heart performance during exercise or medication-induced stress.
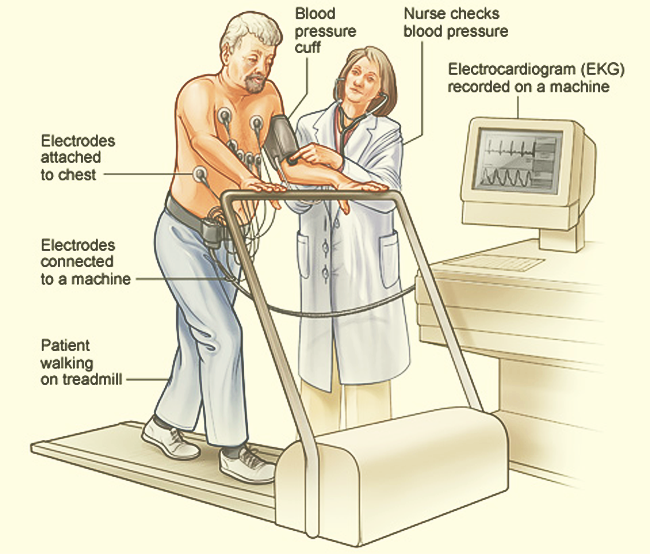
3. stress test (treadmill test)
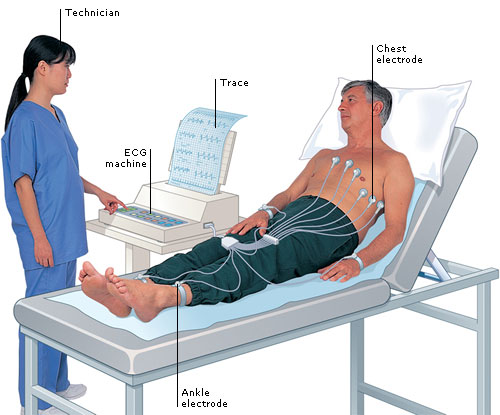
4. ECG
An ECG (electrocardiogram) involves attaching electrodes to specific points on the body to record the heart’s electrical activity. In the image, chest and ankle electrodes are connected to a machine that prints out a trace or waveform. A trained technician operates the ECG machine to monitor and assess the patient’s heart rhythm.
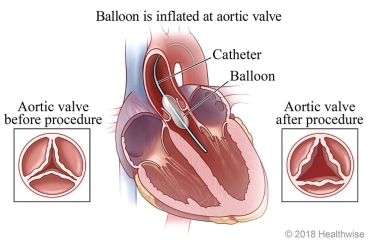
5. Balloon Valvuloplasty
Balloon valvuloplasty is a medical procedure to widen a narrowed heart valve, usually the aortic valve. A balloon-tipped catheter is inserted through a blood vessel and guided to the valve, then inflated to open it. As shown in the image, the valve opens wider after the procedure, improving blood flow and relieving symptoms.
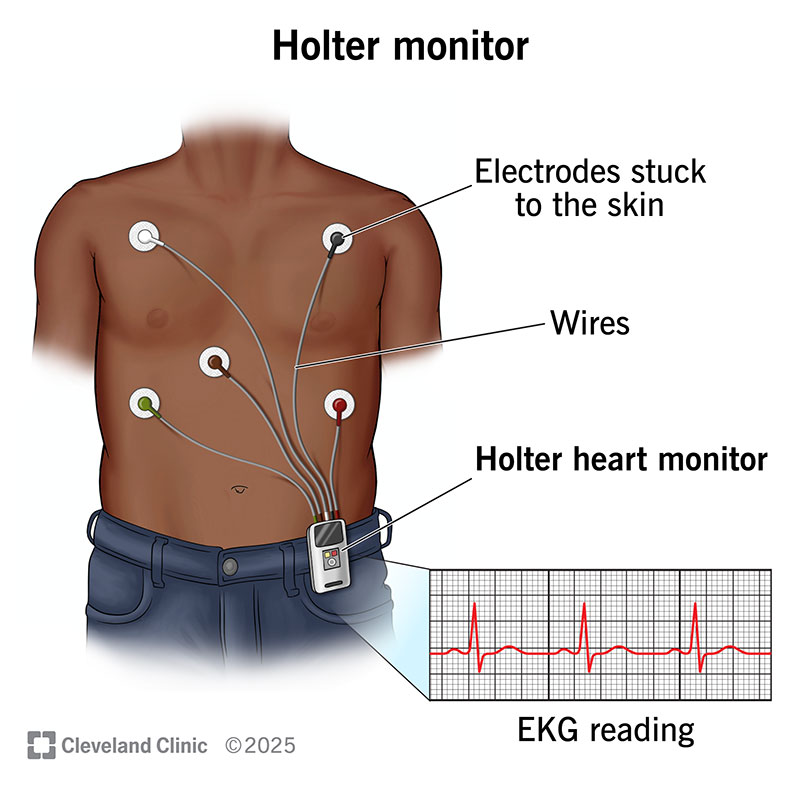
6. Holter study
A Holter monitor is a portable device used to track your heart’s activity over 24–48 hours. Electrodes are attached to the chest and connected by wires to the monitor clipped at the waist. It records continuous EKG readings to help doctors detect irregular heart rhythms missed during a regular ECG.
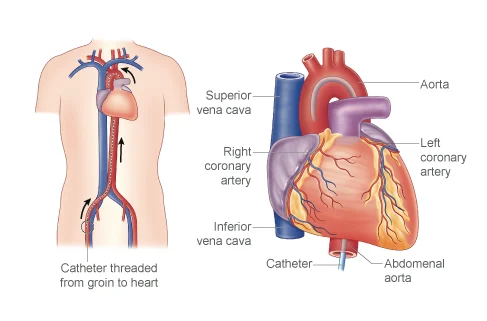
7. coronary angiography & angiography
Angiography is a diagnostic test that uses dye and X-rays to check blood flow in arteries and veins. Coronary angiography specifically focuses on heart arteries, using a catheter threaded from the groin to the heart. It helps doctors spot blockages and plan treatments like stenting or surgery to restore healthy blood flow.
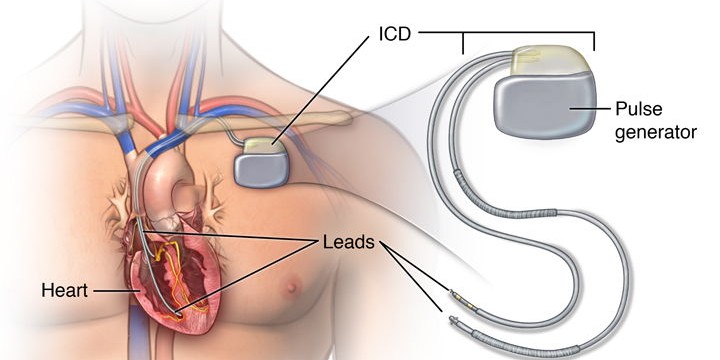
8. permentant pacemaker & ICD implamentation
A pacemaker or ICD (Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator) is placed under the skin to regulate heartbeats. Leads from the device are connected to the heart to deliver electrical impulses when needed. While a pacemaker helps manage slow rhythms, an ICD also delivers shocks during life-threatening arrhythmias.
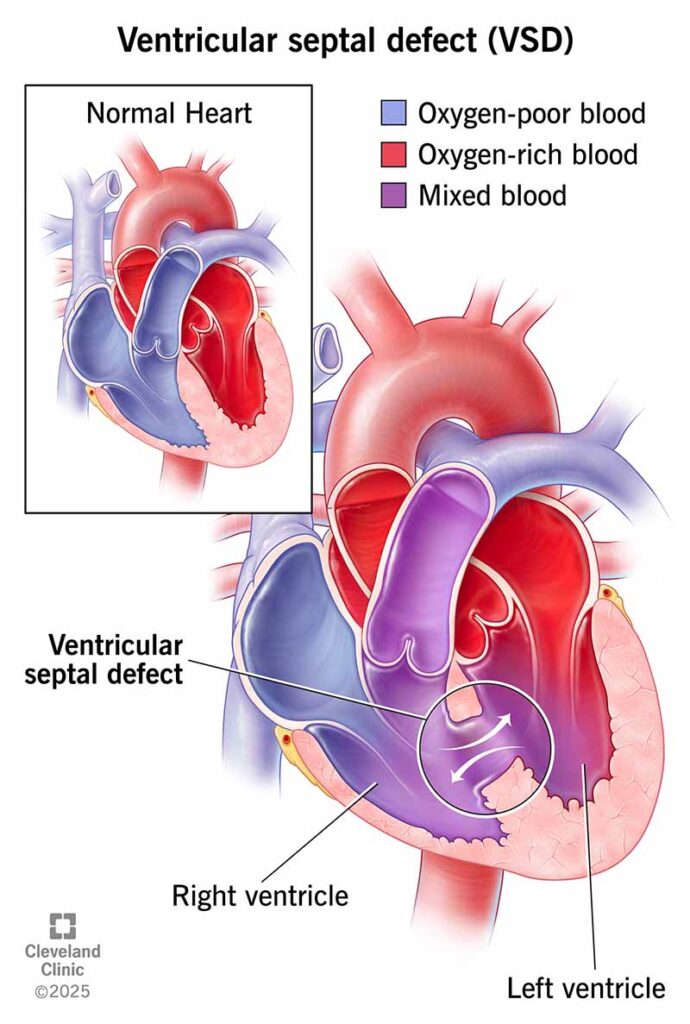
9. Device Closure of Pediatrics Heart Defects ( ASD/ VSD/PDA )
Device closure is a minimally invasive procedure to correct heart defects like ASD, VSD, or PDA in children. A catheter is inserted through a vein and guided to the heart, where a closure device seals the defect. This method avoids open-heart surgery, promoting faster recovery and fewer complications.

